Physics class 12 handwritten notes ,pdf free download
What is a Capacitor?
Capacitors are also known as Electric-condensers. A capacitor is a two-terminal electric component. It has the ability or capacity to store energy in the form of electric charge. Capacitors are usually designed to enhance and increase the effect of capacitance. Therefore, they take into account properties like size and shape. The storing capacity of capacitance may vary from small storage to high storage.
Capacitance
Capacitance is nothing but the ability of a capacitor to store the energy in form of electric charge. In other words, the capacitance is the storing ability of a capacitor. It is measured in farads.
Construction of Capacitor
Most capacitors usually contain two electrical conductors. These conductors are separated by metallic plates. Conductors may be in form of electrolyte, thin film, a sintered bead of metal etc.
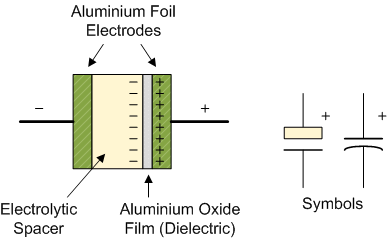 |
| jee forum |
Characteristics of Capacitors
The properties or characteristics of capacitors may differ from one another. Few characteristics of capacitors are:
Capacitance (C)
Capacitance is the basic and important characteristic of a capacitor. We measure it in pico-Farads (pF), nano-Farads (nF) or micro-Farads (µF). Usually, we can find this value printed on the capacitor body in form of a number or text. Hence, you can get this value easily. You can see capacitance in the Solved example below.
Working Voltage
The total amount of direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC) is applied to a capacitor without any failure in the capacitor’s whole lifetime. Working Voltage defines this statement.
Tolerance
Just like the voltage rating, capacitors also have a tolerance rating. They vary from plus to minus value.
Leakage Current
The capacitors Leakage Current is the small DC current flow in the region of Nano-Amps (nA). Leakage current is a result of electrons physically making their way through the dielectric medium. It could also be the movement around its edges or across its leads. Therefore, these electrons can fully discharge the capacitor over time if you remove the supply voltage.
You can download Capacitors and Capacitance Cheat Sheet by clicking on the download button below
Download pdf for free
| Header | Header | Header |
|---|---|---|
| Chapter :-1 | Electric charge | Download |
| Chapter :-2 | Electric field | Download |
| Chapter :-3 | Electrostatic potential and flux | Download |
| Chapter :-4 | Capacitance | Download |
| Chapter :-5 | Electric current and resistance | Download |
| Chapter :-6 | Electrical measurement | Download |
| Chapter :-7 | Heating effect of electric current | Download |
| Chapter :-8 | Magnetic field due to electric current | Download |
| Chapter :-9 | Motion of charged particles in electric and magnetic fields |
Download |
| Chapter :-10 | Magnets and earth magnetism | Download |
| Chapter :-11 | Electromagnetic induction | Download |
| Chapter :-12 | Alternating current | Download |
| Chapter :-13 | Reflection of light | Download |
| Chapter :-14 | Refraction of light | Download |
| Chapter :-15 | Dispersion of light | Download |
| Chapter :-16 | Optical instrument | Download |
| Chapter :-17 | Huygen's principle and interference | Download |
| Chapter :-18 | Diffraction and polarisation | Download |
| Chapter :-19 | 19.semi conductor | Download |
| Chapter :-20 | Dual nature of light | Download |





1 Comments
hello...good1
ReplyDelete